Another Halving is at the door. Expected on the 12th of May, the reward the miners will receive for securing the network in the form of newly created Bitcoins will be halved. What are the consequences of this event? In this paper we will offer the most important information at a glance.
What is the halving?
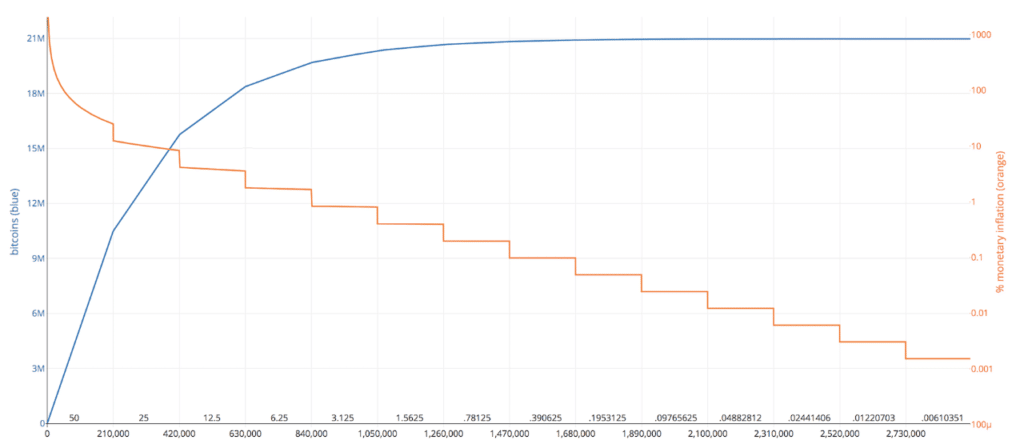
Bitcoin as a digital currency has predetermined limits on the supply side. For example, the maximum number of Bitcoins anchored in the code is limited to 21 million. Of these, just under 18.32 million coins are currently already in circulation. Newly created Bitcoins are paid to the miners, who contribute computing power to ensure the blockchain system. This reward is halved every 4 years, hence the term “halving”. Accordingly, the number of newly created Bitcoins is steadily reduced until, purely mathematically, the maximum amount of 21 million Bitcoins is reached in 2140. We are therefore facing the third halving in the history of Bitcoin. The original reward for “mining” was 50 BTC per block created. In November 2012 it was 25 BTC and by July 2016 it was 12.5 BTC. As of May 12, 6.25 BTC will be paid for each block created.
What effect does halving have on the Bitcoin price?
Bitcoin is designed as a limited digital good, similar to silver or gold. Its price depends on supply and demand. Halving means that fewer Bitcoins come into circulation, making supply scarcer. The output speed or the inflation rate is increasingly reduced.
Currently, about 1,800 new Bitcoins worth a good $16 million are created and distributed to the miners every day. For their part, the miners usually sell a large part of the rewards they receive in the form of Bitcoins to finance their infrastructure. The market therefore had a newly created daily supply of 1800 Bitcoins to absorb over the last four years. This offer will be cut in half next week and theoretically only 8 instead of 16 million USD per day will come on the market at the current rate.
In the medium term, a supply shortage is fundamentally positive, according to a principle in the financial markets – rarity increases value. One approach which brings this thesis to bear is the stock-to-flow model. In the short term it is difficult to speculate on a “halving”. During the last few halvings, a “buy the rumor sell the fact” behavior was observed in the market. However, bitcoin experienced a massive price increase especially after the last halvings.
Effect on the perception and reach of bitcoin and crypto currencies
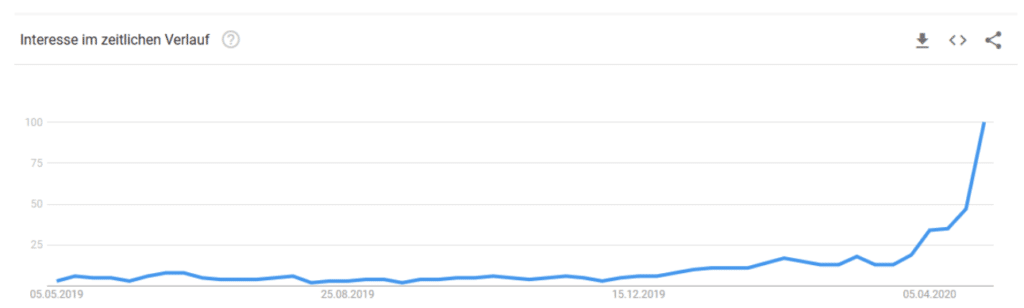
A noticeable upturn can already be observed on Google after the search term “Bitcoin Halving”. Due to the increase in the global money supply, a contrary concept inevitably leads to interest. Last but not least, investors interested in hard assets like gold will sooner or later stumble upon Bitcoin. The halving brings Bitcoin’s presence back onto the trading floor and leads to increased interest.
Of course, speculation is also a factor why more people are interested in the crypto currency again around Halving events. The last two halvings have led to new all-time highs of the Bitcoin exchange rate in the months following.
What does halving mean for the Bitcoin mining industry?
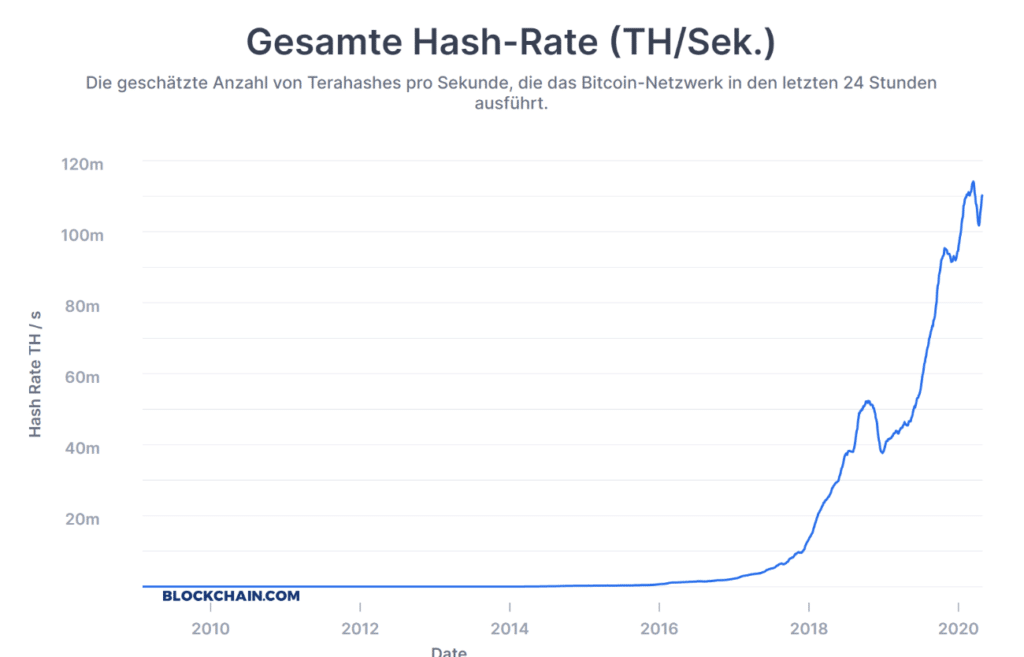
Bitcoin mining requires a large amount of energy. On the one hand for performing the calculations and on the other hand for cooling the computers that perform these operations. The mining industry therefore mainly prioritizes locations where cheaper electricity is available. The cost of Bitcoin Mining is between $3,500 and $6,500, depending on the cost of equipment, electricity and the real estate used to house the hardware. If the miners are halved, the price of Bitcoin has to double to return to the pre-halving level. Despite the past two halvings, the total computing power available to the network has been rising for years and is close to its all-time high (see next section).
The sector is therefore in constant competition. This competition is undoubtedly intensified by halving. Compared to the last halving in July 2016, however, the following can be noted: There are more major players in mining, more efficient mining equipment and more competition than ever before. A large proportion of the mining companies are located in China, but Canada, Iceland and the USA are also involved. After halving, some miners are likely to switch off their computers in the short term due to profitability. If the Bitcoin price rises again in the future, more miners will return to the market.
What role do the miners play and how do they influence the Bitcoin network
In a Proof of Work consensus algorithm on which the Bitcoin network is based, computers must solve a specific type of mathematical problem (or millions of them). The calculations required to “build” a block are sometimes performed almost exclusively by application specific devices (ASIC). ASIC systems are manufactured with the aim of enabling more efficient and faster production in a specific field.
Bitcoin mining is based on the SHA-256 algorithm. Block production requires complex computing operations. A mathematical puzzle must be solved for this. For this, thousands or even millions of “hashes” are made per second to find the right answer to solve the block. The hash rate is the measuring unit of this computing power and is measured in terahashes TH (1 trillion hashes) per second. The hash rate of the Bitcoin network is therefore the total power of the participating mining devices. This shows how many operations per second are available for mining.
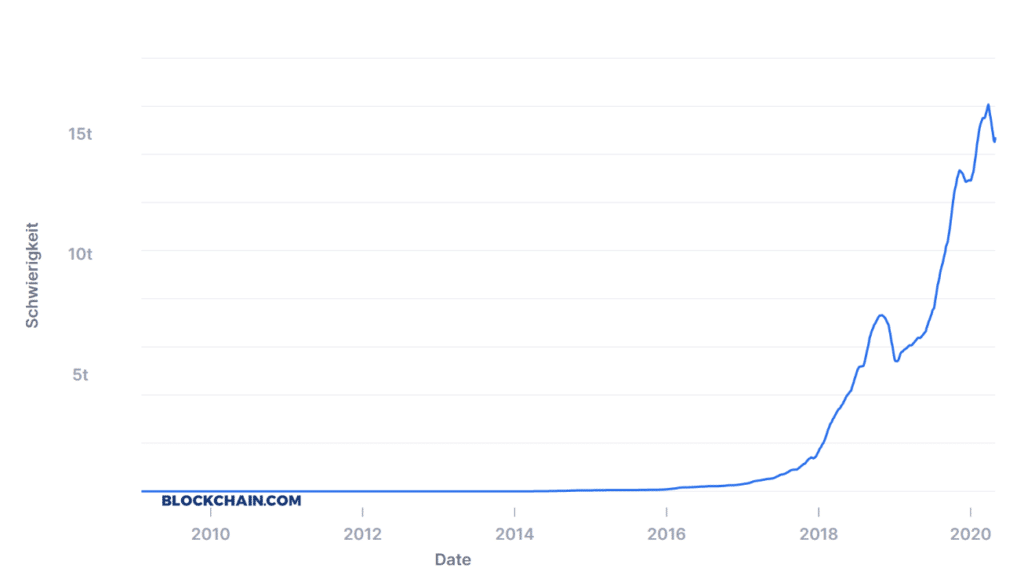
To ensure block times of around 10 minutes, adjustments to the calculation difficulty are made every two weeks in the Bitcoin network. Difficulty is a parameter used by Bitcoin and other PoW crypto currencies to keep the average time between blocks constant if the hash performance of the network changes. Simply put, the more hashing power, the higher the Difficulty Rate. If the number of miners or the computing power in the network decreases, the difficulty of the block calculations is reduced. The following diagram of the difficulty correlates very closely with the total hash rate in the network.
Bitcoin Halving Webinar Thursday 7 May 4 pm
Would you like to learn more about Bitcoin and the Halving? Please join the online information event of our partner CV Labs on May 7th. Blockchain and financial experts from Crypto Valley will guide you through the program.
*Originally published in German at CVJ.ch